注釈
Go to the end to download the full example code.
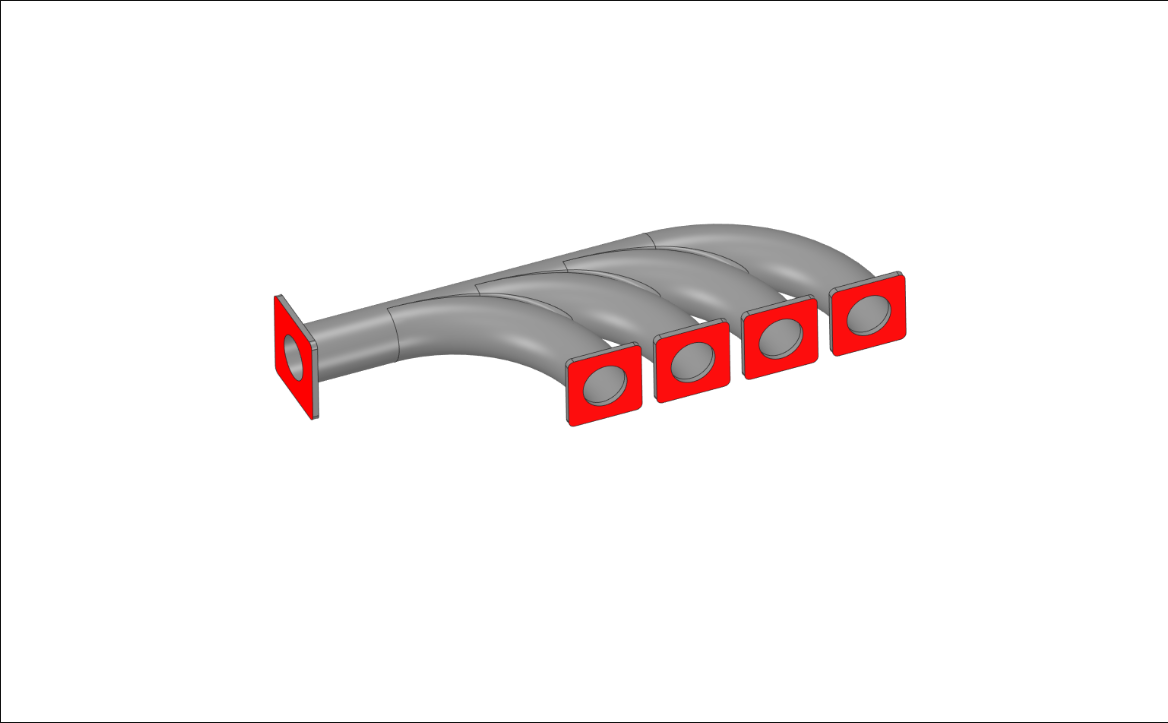
Thermal-structural analysis of exhaust manifold#
This example illustrates how to map results from a CFD analysis and perform a Finite Element (FE) analysis.
Objective#
In this example, we will perform an FE analysis to compute the thermal stresses developed in an exhaust manifold. The manifold is made of structural steel and the temperature distribution in it is obtained from a CFD run. We import this data and map it onto FE mesh to define thermal load at each node using Gaussian interpolation kernel.
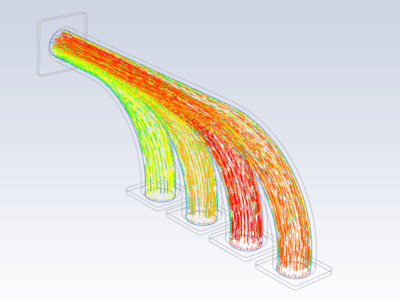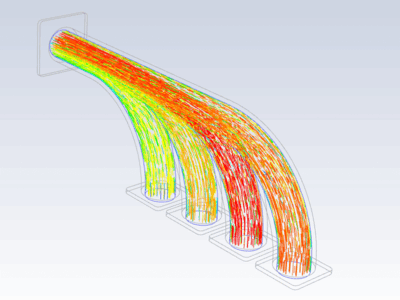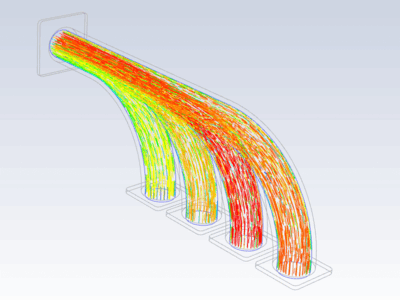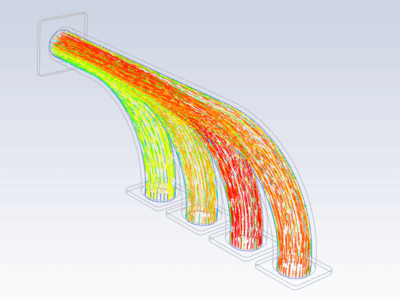
Procedure#
Launch MAPDL instance
Import geometry, assign material properties, and generate FE mesh.
Import temperature distribution and map it on FE mesh
Define BCs and use imported temperature distribution to define thermal load.
Solve the model and plot the results of interest.
Additional Packages used#
Boundary Conditions#
Highlighted faces are fully constrained.
Import all necessary modules and launch an instance of MAPDL#
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import pyvista as pv
from ansys.mapdl.core import launch_mapdl
from ansys.mapdl.core.examples import download_manifold_example_data
# start mapdl
mapdl = launch_mapdl()
print(mapdl)
Import geometry, assign material properties and generate a mesh.#
# download the necessary files
paths = download_manifold_example_data()
geometry = paths["geometry"]
mapping_data = paths["mapping_data"]
# reset mapdl & import geometry
mapdl.clear()
mapdl.input(geometry)
# Define element attributes
# Second-order tetrahedral elements (SOLID187)
mapdl.prep7()
mapdl.et(1, "SOLID187")
# Define material properties of structural steel
E = 2e11 # Youngs modulus
NU = 0.3 # Poisson's ratio
CTE = 1.2e-5 # Coeff. of thermal expansion
mapdl.mp("EX", 1, E)
mapdl.mp("PRXY", 1, NU)
mapdl.mp("ALPX", 1, CTE)
# Define mesh controls and generate mesh
mapdl.esize(0.0075)
mapdl.vmesh("all")
# Save mesh as VTK object
print(mapdl.mesh)
grid = mapdl.mesh.grid # save mesh as a VTK object
Import and map temperature data to FE mesh#
# Import csv file and save data to a NumPy array
temperature_file = pd.read_csv(mapping_data, sep=",", header=None, low_memory=False)
temperature_data = temperature_file.values # Save data to a NumPy array
nd_temp_data = temperature_data[1:, 1:].astype(float) # Change data type to Float
# Map temperature data to FE mesh
# Convert imported data into PolyData format
wrapped = pv.PolyData(nd_temp_data[:, :3]) # Convert NumPy array to PolyData format
wrapped["temperature"] = nd_temp_data[
:, 3
] # Add a scalar variable 'temperature' to PolyData
# Perform data mapping
inter_grid = grid.interpolate(
wrapped,
sharpness=5,
radius=0.0001,
strategy="closest_point",
progress_bar=True,
) # Map the imported data to MAPDL grid
inter_grid.plot(show_edges=False) # Plot the interpolated data on MAPDL grid
temperature_load_val = pv.convert_array(
pv.convert_array(inter_grid.active_scalars)
) # Save temperatures interpolated to each node as NumPy array
node_num = inter_grid.point_data["ansys_node_num"] # Save node numbers as NumPy array
Apply loads and boundary conditions and solve the model#
# Read all nodal coords. to an array & extract the X and Y min. bounds
array_nodes = mapdl.mesh.nodes
Xmin = np.amin(array_nodes[:, 0])
Ymin = np.amin(array_nodes[:, 1])
# Enter /SOLU processor to apply loads and BCs
mapdl.finish()
mapdl.slashsolu()
# Enter non-interactive mode to assign thermal load at each node using imported data
with mapdl.non_interactive:
for node, temp in zip(node_num, temperature_load_val):
mapdl.bf(node, "TEMP", temp)
# Use the X and Y min. bounds to select nodes from five surfaces that are to be fixed and created a component and fix all DOFs.
mapdl.nsel("s", "LOC", "X", Xmin) # Select all nodes whose X coord.=Xmin
mapdl.nsel(
"a", "LOC", "Y", Ymin
) # Select all nodes whose Y coord.=Ymin and add to previous selection
mapdl.cm("fixed_nodes", "NODE") # Create a nodal component 'fixed_nodes'
mapdl.allsel() # Revert active selection to full model
mapdl.d(
"fixed_nodes", "all", 0
) # Impose fully fixed constraint on component created earlier
# Solve the model
output = mapdl.solve()
print(output)
Post-processing#
# Enter post-processor
mapdl.post1()
mapdl.set(1, 1) # Select first load step
mapdl.post_processing.plot_nodal_eqv_stress() # Plot equivalent stress
Exit MAPDL instance#
mapdl.exit()

